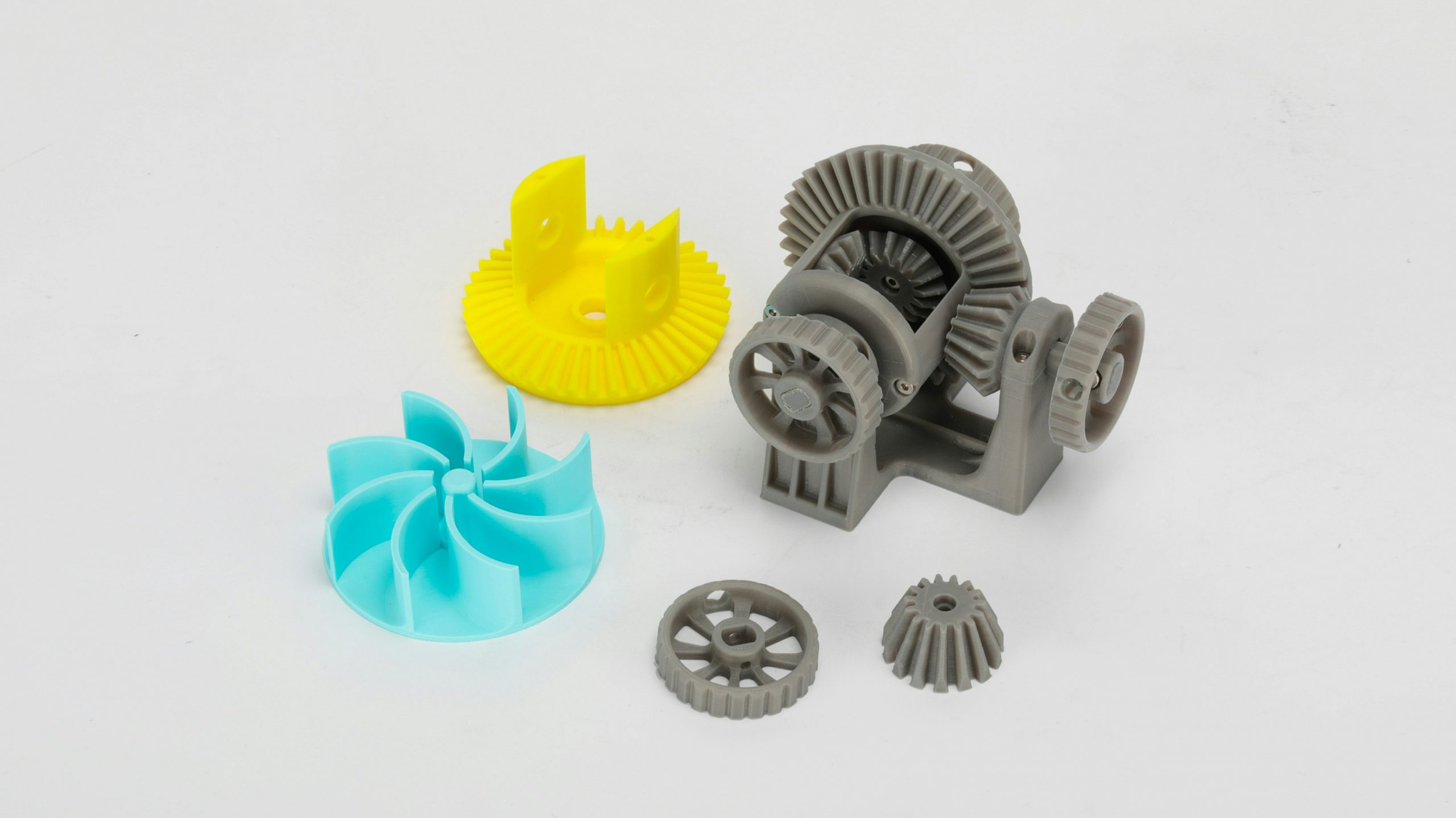
Flexibility Comparison Chart
| Material | Flexibility Level | Relative Stiffness | Typical Shore Hardness | Bend / Flex Capability | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLA | Very Low | Very Rigid | Shore D 80–85 | Minimal – brittle under stress | Rigid parts, display items, precision components |
| PETG | Low | Semi-Rigid | Shore D 75–80 | Slight flex before deformation | Functional parts, mounts, enclosures |
| ABS | Low–Medium | Rigid with toughness | Shore D 70–78 | Slight flex, good impact resistance | Housings, tooling, high-temp parts |
| TPU | High | Flexible / Elastic | Shore A 85–95* | Significant flex, compresses and rebounds | Gaskets, bumpers, flexible mounts |
* Exact Shore hardness depends on TPU formulation used.
Material Flexibility Summary
- PLA – Best for rigid, dimensionally accurate parts with no flex requirements
- PETG – Slightly flexible but primarily used as a tough rigid material
- ABS – Rigid with improved impact resistance, limited flex
- TPU – Designed for flexibility, elasticity, and vibration absorption
Print Layer UK Recommendation
If flexibility, shock absorption, or repeated bending is required, TPU is the preferred material. For structural rigidity and dimensional stability, PLA, PETG, or ABS are more suitable depending on temperature and load requirements.
Share this content: